What is a Care Plan for Nursing?
A care plan for nursing, also referred to as a nursing care plan can be defined as:
A formal process that encompasses correct identification of existing nursing patient needs and recognition of potential needs of nursing patient risks.
Note that care plans are used as communication tools between nurses, patients under care, and relevant healthcare providers to help realize consistency and quality in health care outcomes.
The process of writing a nursing care plan is as explored hereunder.
Writing a Nursing Care Plan
Skills on how to write a care plan for nursing requires knowledge on the diagnosis process.
Per se, developing NANDA nursing care plans demands that you utilize nursing diagnosis to determine the suitable plan of care for a particular patient.
In this case, a nursing care plan is:
- A written record of an action plan developed with a patient to meet their social and health needs.
- A plan that outlines who is doing what, at what time (when), and for what reasons (why)-It provides aims, actions, and responsibilities.
- A tool supporting patient and health provider safety.
- A plan that can be relied on and easily understood by care providers, family members, and other relevant parties during crisis.
- A plan founded on comprehensive assessment of needs.
- A plan produced in consultation and shared with all the involved parties.
- Part of a support process for planning systems like Care Program Approach, Care and Treatment Planning, Long Term Conditions Planning, etc.
Categories of Care Plans for Nursing
When it comes to how to write a care plan for nursing, it is important to understand the available options. Nursing care plans can be grouped into 4 major categories, including:
- Informal care plan for nursing
- Formal care plan for nursing
- Standardized care plans
- Individualized care plans
Objectives of a Care Plan for Nursing
NANDA nursing care plans should be guided by specific objectives. Such objectives may encompass:
- Supporting holistic care, including psychological, physical, spiritual, and social elements of individual health.
- Promoting evidence-based nursing care.
- Establishing care programs like care bundles and care pathways.
- Enhancing good and familiar conditions within health care establishments.
- Reviewing documentation and communication of a care plan.
- Assessing nursing care.
Components of a Care Plan for Nursing
Effective skills on how to write a care plan for nursing involves a good understanding of the different components of care plans.
As illustrated in NANDA nursing care plan examples, all care plans constitute different components. These components indicate the various areas the care plan should focus on. They include:
1. Assessment
This entails respective diagnostic reports and medical results. Assessment is a primary component in the design of a care plan.
It should entail all facets of a patient’s well-being, including physical, cognitive, psychological, emotional, spiritual, cultural, sexual, environmental, and economic factors.
2. Diagnosis
This involves a summary of the current health status of the patient as is derived from the patient’s response to a particular health condition.
As illustrated in various nursing care plan examples, it also defines what the nurse can contribute in care provision.
3. Care plan goals
When it comes to how to write a care plan for nursing, care plan goals encompass clear, concise, and realistic description of the intervention’s desired outcomes.
They could be long-term or short-term. Importantly, they should be measurable.
4. Interventions
These entail all the treatment done to help realize the set goals or desired outcomes.
5. Outcomes
These involve the expectations on the patient. It is how the patient is supposed to react to the intervention.
The outcome should be realistic and measurable.
6. Evaluation
This entails periodical review of the patient’s goals and outcomes.
It should compare actual outcomes with predicted ones, review interventions, and where need be, modify the care plan.
Format of a Care Plan for Nursing
Just like in the case of nursing essays and research papers, writing a care plan for nursing should be evidence based.
That said, format is very important when it comes to how to write a care plan for nursing. Note that the format could vary depending on whether you are a practicing nurse or a nurse student.
In both cases, you have to adhere to the respective standards for NANDA nursing care plans.
Note that for the practicing nurse however, you may not be required to include components like assessment, rationale, and evaluation.[nbsp][nbsp]
In line with common nursing care plan examples, the care plan format for nursing students could be as illustrated below.
| [nbsp]Assessment | [nbsp]Diagnosis | [nbsp]Outcomes | [nbsp]Interventions | [nbsp]Rationale | [nbsp]Evaluation |
| [nbsp]Dyspnea presence[nbsp][nbsp]Presence of breath sounds that are abnormal[nbsp][nbsp]128bph for Heart rate[nbsp][nbsp]Restlessness[nbsp][nbsp]Presence of productive cough | [nbsp]RT gas exchange[nbsp] that is impaired[nbsp][nbsp]Mucus collection in airways | [nbsp]Maintenance of[nbsp] optimal gas[nbsp] exchange by the[nbsp] patient | [nbsp]1.Respiration assessment:[nbsp]Note quality, depth, rate, rhythm, accessory muscles use, and easy breathing assumed position. | [nbsp]1.Respiratory distress manifestations depend on and indicate lung involvement degree as well as the general health status since patients adapt their patterns of breathing to allow effective exchange of gas.[nbsp]2.The measure are meant to support maximum expansion of the chest, secretions mobilization, and ventilation improvement. | [nbsp]Maintenance of optimal gas exchange AEB normal respiratory rate, absence of dyspnea, and coughing techniques that are effective. |
Nursing Care Plan for a Nurse Student[nbsp]
Note that although you can use the above nursing care plan template for most student assignments, the nursing care plan requirements may however change from one institution to another.
Also, for professional practice, care plans could be different as well. Such care plans usually omit 2 or 3 areas from the student care plan.
As illustrated in standard NANDA nursing care plan examples, some of the most commonly omitted areas include assessment and rationale.[nbsp] [nbsp][nbsp]
A nursing care plan template for professional nurse could be as illustrated below.
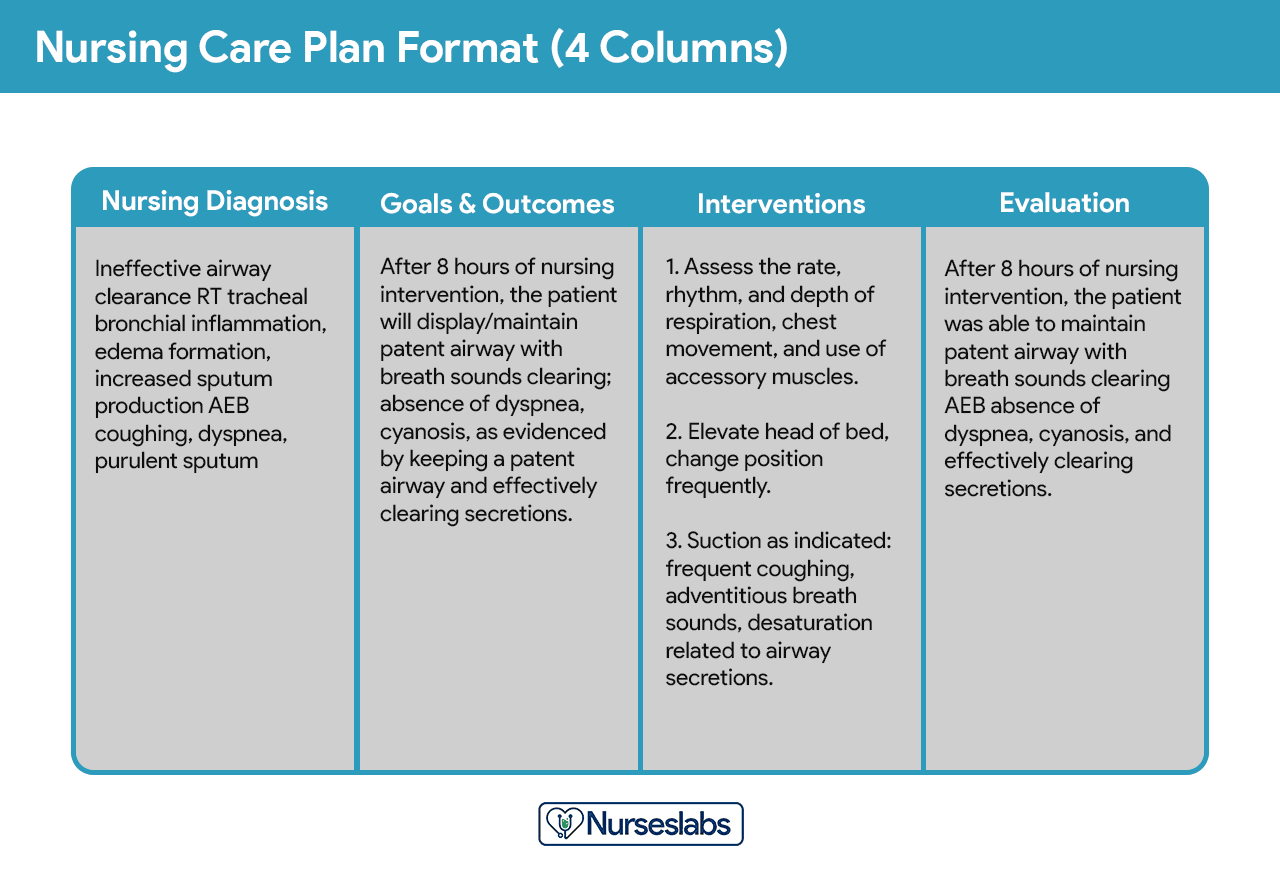
Nurselabs: 4-Column Nursing Care Plan[nbsp]
[nbsp]
Steps on How to Write a Care Plan for Nursing
The process of writing nursing care plans is quite simple. Note that despite the slight difference evident in various nursing care plan examples, the entailed steps are usually common.
Per se, the writing process is defined by the below steps.
Step 1: Data Collection
This entails the first step of the nursing care plan writing process. In this step, you are required to create a patient database using data acquired through appropriate patient assessment techniques as well as data collection methods.
Such techniques and methods may include diagnostic studies, interviews, health history review, physical assessment, and review of medical records. The database should include all information that is possible to acquire.
During the assessment, it is important to go ahead and isolate the entailed risk factors, as well as define the different characteristics key to nursing diagnosis formulation.
Step 2: Data Analysis
This is a very instrumental step when it comes to how to write a nursing diagnosis. It entails analyzing, clustering, and organizing acquired patient data in order to come up with the right nursing diagnosis, nursing priorities, and preferred outcomes.
It is important to ensure that all information is considered in the analysis. In this, the analysis should examine the areas the patient is experiencing health problem in.
While analyzing the data, it is critical to think about ways in which the patient can improve. Also think of ways to evaluate the improvements.
During the process, the nurse should note down general issues entailed in the patient’s problem.
Step 3: Nursing Diagnoses Formulation
In this step, it is advisable to observe the guidelines provided for NANDA nursing diagnoses. These guidelines provide for a uniform method for ascertaining, paying attention to, and handling client needs.
These guidelines extend from patient responses to actual/definite and high risk problems.[nbsp][nbsp]
In this case, nursing diagnoses entail actual or prospective health problems that are preventable or resolvable using independent nursing intervention.
Accordingly, this requires knowledge on how to develop nursing diagnoses.[nbsp] [nbsp]
Step 4: Establishment of Priorities
This is equally a very important step when it comes to how to write a nursing diagnosis. As illustrated in NANDA nursing care plan examples, establishing priorities entails coming up with a sequence of activities on how to handle diagnoses and interventions.
This step requires the nurse together with patient to deliberate and agree on the nursing diagnoses that should be attended to first. Here in, prioritization demands the ranking of diagnoses either as high, medium, or low.
Priorities should be accorded life-threatening problems, where they should be ranked as high.
Some of the factors to consider when developing the priorities include patient’s beliefs and values, urgency of the problem, patient’s priorities, and available resources.
Step 5: Goals and Outcomes Determination
As illustrated in different nursing care plan examples, this is usually the last step when writing a nursing care plan.
The nurse in collaboration with the patient should come up with goals for all the established priorities.
These goals entail the desired outcomes and should elaborate what the nurse seeks to achieve through the implementation of nursing interventions that have been derived from the respective nursing diagnoses.
Such goals are usually the direction for planning interventions. They provide the criteria for patient progress evaluation. As such, they should be used by the nurse working together with the patient to establish the problem that require solving.
The goals and outcomes should also be used as a source of motivation for the nurse and the client since they can help indicate achievements.[nbsp] [nbsp][nbsp]
[nbsp]